About a week ago, Google published a blog post titled Understanding web pages better, in which they confirm that Googlebot is indeed executing JavaScript these days, and that they’ve been gradually improving their indexing for it during the last few months.
Shortly after, the company added a new instrument to their Webmaster Tools panel, which shows you exactly what Googlebot sees, when it’s indexing a page. It is aptly named Fetch as Google, and out of curiosity I put it to the test with a simple Ember.js application today.
The test subject
I recently live-coded a small Ember application during a talk at Interactive Cologne, which fits nicely as a test dummy. Bitgogo is a rudimentary crowd-funding app, displaying the balance in a Bitcoin wallet as well as a target and the USD equivalent.
You can check out the code on GitHub; it’s as simple as it gets. There’s a Handlebars template, as well as some code fetching data from two REST APIs during startup (and polling from there on).
(Be sure to also check out our actual Indiegogo campaign for a movie about the East-African tech scene, that we want to create out of the 30+ hours of material we have from a trip through four African countries last fall.)
Fetch as Google in action
And so, without further ado, here’s what Googlebot sees according to Fetch as Google:
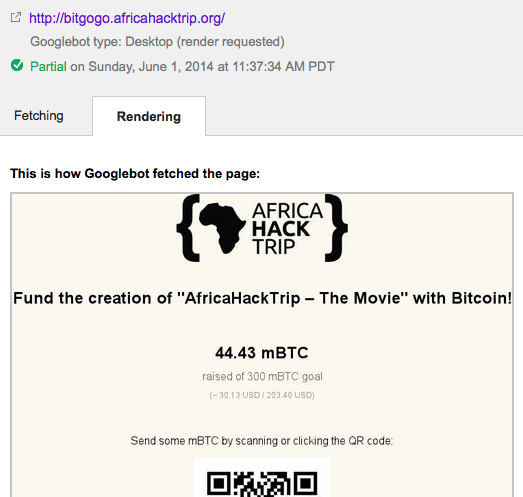
Win!
There you have it: Googlebot successfully rendered the Ember.js application, including the asynchronous fetching and subsequent rendering of the data!
Now, for less advanced search engines, you might still want to pre-render pages on the server, but given that the competition will likely catch up in the near future, it looks to me like rendering Web app content completely on the client-side will not be an SEO problem for too much longer.
